Smoking on Your Dental Health and How to Quit
Smoking is known to have numerous detrimental effects on overall health, and your dental health is no exception. Tobacco use significantly increases the risk of oral health issues, including gum disease, tooth decay, and oral cancer. In this article, we will explore how smoking affects your dental health and provide helpful strategies for quitting.
1. How Smoking Affects Your Dental Health
A. Gum Disease
One of the most significant consequences of smoking on your dental health is the increased risk of gum disease (periodontitis). Smoking weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infections in the gums. This leads to a higher likelihood of developing gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease, and progressing to periodontitis, which can cause tooth loss. Smokers are twice as likely to develop gum disease as non-smokers.
B. Tooth Decay and Cavities
Smoking also contributes to tooth decay and cavities. The chemicals in tobacco reduce saliva production, which is crucial for neutralizing acids and protecting teeth from decay. Additionally, smoking causes plaque and tartar buildup, which further increases the risk of cavities. The sticky substances in tobacco can also stain your teeth, leading to yellow or brown discoloration.
C. Oral Cancer
Smoking is a leading cause of oral cancer, with smokers being six times more likely to develop cancers of the mouth, throat, and tongue than non-smokers. The carcinogens in tobacco directly damage the cells of the mouth, leading to an increased risk of developing cancerous lesions and growths. Early detection through regular dental checkups is essential for those who smoke.
D. Bad Breath
Tobacco use causes persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis. The smell of tobacco and the chemicals it leaves behind in the mouth contribute to an unpleasant odor. In addition, smoking dries out the mouth, which allows bacteria to thrive and further contributes to foul-smelling breath.
Guidance for Informed Choices
Whether navigating healthcare or entertainment options, having access to a trusted casino review helps ensure safe and enjoyable experiences. Reliable information is key to making the best decisions.
2. How Smoking Affects Healing After Dental Procedures
Smokers also face challenges when it comes to healing after dental procedures. Whether it’s a tooth extraction, gum surgery, or dental implants, smoking can interfere with the body’s natural healing process. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the gums and other tissues. This delayed healing can increase the risk of infection and complications after dental procedures.
3. How to Quit Smoking for Better Dental Health
A. Set a Quit Date
The first step in quitting smoking is to set a quit date. Choose a date within the next two weeks to allow yourself enough time to prepare and set goals. Mark it on your calendar and make a commitment to yourself that you’ll take action to improve your health.
B. Seek Support
Quitting smoking is a challenging process, but you don’t have to do it alone. Seek support from family, friends, or a healthcare provider. Consider joining a support group or seeking counseling to manage cravings and triggers effectively.
C. Use Smoking Cessation Aids
Nicotine replacement therapies, such as nicotine patches, gum, or lozenges, can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. In some cases, prescription medications may also help people quit smoking. Speak with your doctor or dentist about which options are right for you.
D. Replace Smoking with Healthier Habits
Replace the habit of smoking with healthier alternatives. For example, exercise can help reduce stress and manage cravings. Additionally, practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help you manage triggers that make you want to smoke. Drinking plenty of water and chewing sugar-free gum can also help keep your mouth fresh and reduce the urge to smoke.
4. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene While Quitting
As you work toward quitting smoking, maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential to counteract the negative effects smoking has had on your dental health. Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. This will help prevent further damage and improve your overall oral health as you transition to a smoke-free life.
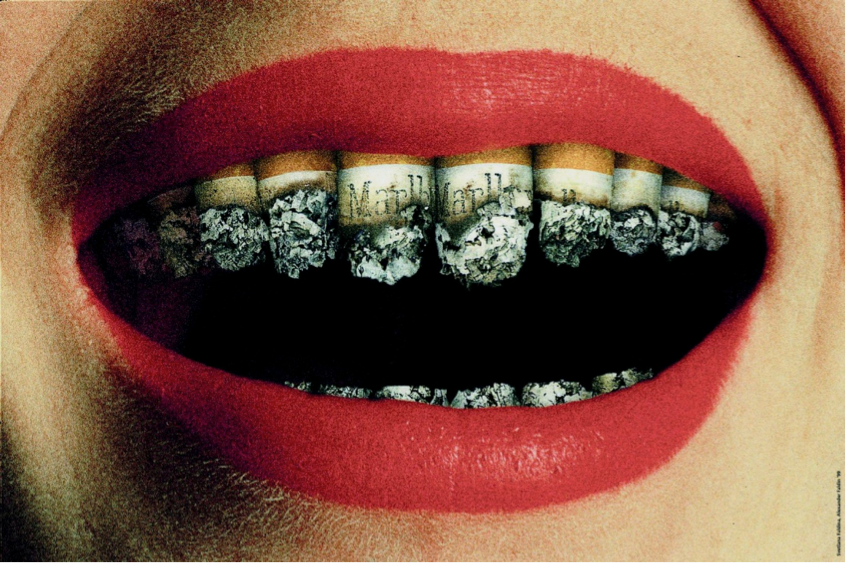
5. Conclusion: A Smoke-Free Future for Your Dental Health
The impact of smoking on dental health is significant, but the good news is that quitting can significantly improve your oral health and reduce your risk of developing serious dental issues. By understanding the risks and implementing strategies for quitting, you can take control of your health and achieve a brighter, healthier smile. If you are considering quitting smoking, talk to your dentist for personalized advice and support.
“`html
Achieve Wellness with Dr. Catherine Fulton
Dr. Catherine Fulton offers personalized healthcare services focused on holistic wellness, helping individuals achieve optimal physical and mental health. Through evidence-based treatments and compassionate care, she empowers clients to live healthier, happier lives. Take the first step toward better health today. https://www.gambling360.com/casino-bonus/.
“`